[자료구조] 4.1 연결 리스트의 개념적인 이해 (2)
Updated:
연결 리스트의 개념적인 이해 (2)
연결 리스트
연결리스트 개념 - 예제(LinkedRead.c)
node.date : 데이터 저장 node.next : 다음 node의 주소값 저장
초기화
typedef struct _node {
int data;
struct _node * next;
} Node;
int main(void) {
Node * tail = NULL;
Node * cur = NULL;
Node * newNode = NULL;
int readData;
}
- head : 앞 노드를 가리키는 pointer 변수
- tail : 뒤 노드를 가리키는 pointer 변수
- cur : 참조&조회에 필요. 순차적 조회시 사용하는 pointer 변수
-
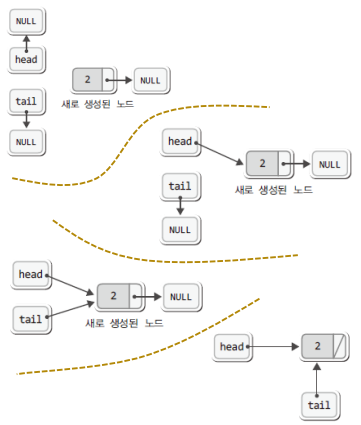
데이터 삽입
while(1)
{
printf("자연수 입력: ");
scanf("%d", &readData);
// 데이터 입력
if(readData < 1) {
break;
// 입력받을 데이터 없으면 break;
}
// 노드 추가과정---------------
newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// malloc 함수로 메모리 동적 할당
newNode->data = readData;
// 새 노드에 데이터 입력
newNode->next = NULL;
// 다음 노드 연결 포인터는 null
if(head == NULL) {
//첫번째 노드의 경우
head = newNode;
} else {
tail->next = newNode;
// tail이 다음 노드를 가리키게 됨
}
tail = newNode;
// 마지막노드 주소값
}
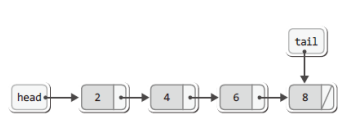
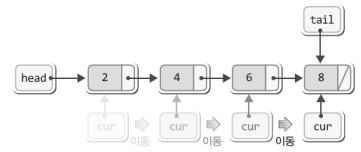
데이터 조회
if(head == NULL) {
printf("저장된 자연수가 존재하지 않습니다. \n");
} else {
cur = head;
// cur이 첫번째부터 접근
printf("%d ", cur->data);
// 데이터 출력
while(cur->next != NULL) {
cur = cur->next;
// cur을 next로 초기화
printf("%d ", cur->data);
//두번째부터 마지막까지 반복
}
}
데이터 삭제
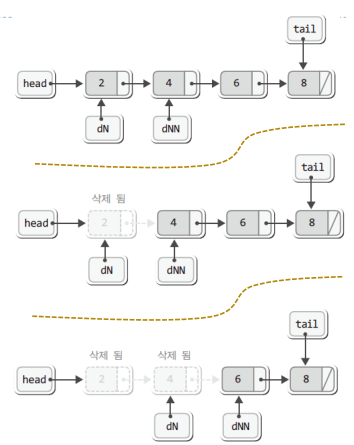
// 전체 노드 삭제------------------
if(head == NULL) {
// 삭제할 노드가 있는지 확인
return 0;
} else {
Node * delNode = head;
Node * delNextNode = head->next;
// head를 next 값으로 변경
printf("%d을(를) 삭제합니다. \n", head->data);
// 노드 데이터 삭제
free(delNode);
// 메모리 할당 해제
while(delNextNode != NULL) {
// 다음 노드 확인
delNode = delNextNode;
delNextNode = delNextNode->next;
printf("%d을(를) 삭제합니다. \n", delNode->data);
// 다음 노드 삭제
free(delNode);
// 메모리 할당 해제
}
}

Leave a comment